The Science Behind Producing High-Quality sugar cane products from Field to Factory
The Science Behind Producing High-Quality sugar cane products from Field to Factory
Blog Article
A Deep Dive Into Sugar Cane: Insights on Production, Supplies, and Item Advancement
Sugar cane plays a vital role in agriculture, underpinning economies in tropical regions. Its cultivation entails complex processes influenced by various environmental elements. However, growers deal with significant difficulties, including climate change and market variations. Developments in product development are emerging in reaction to developing consumer needs. Comprehending these dynamics is important for realizing the future of this crucial plant and its influence on international markets. What exists ahead for sugar cane and its myriad applications?
The Value of Sugar Cane in Global Agriculture
Sugar cane offers as an essential crop in international farming, underpinning economic climates and food systems in several exotic areas. This flexible plant is mostly grown for its high sucrose content, which is improved right into sugar, a staple component in many food. Beyond sweetening, sugar cane is likewise crucial for generating biofuels, particularly ethanol, adding to power sustainability.The financial importance of sugar cane extends to work, offering livelihoods for numerous farmers and employees in processing facilities. In several nations, sugar cane cultivation and handling stand for significant portions of agricultural GDP, affecting trade equilibriums and regional development.Additionally, sugar cane's versatility to different environments improves its importance as a plant, making certain constant supply in worldwide markets. Its spin-offs, including molasses and bagasse, further expand its utility, making it a vital component in food, energy, and industry. Generally, sugar cane remains a cornerstone of farming performance worldwide.
Growing Procedures: From Growing to Harvest
Growing sugar cane involves a series of well-defined procedures that assure suitable development and return. The growing starts with land preparation, where the dirt is tilled to secure ideal aeration and drainage. Following this, seed cane, which includes fully grown stalks, is picked and reduced right into sections (sugar cane products). These sectors are after that planted in furrows, making certain proper spacing to permit sunlight and nutrient access.Once grown, watering systems are used to keep appropriate moisture degrees, as sugar cane thrives in humid problems. Weeding and bug management are necessary throughout the expanding duration to minimize competition for sources. Nutrient application, consisting of fertilizers, supports durable growth. As the plants grow, keeping track of for conditions and insects continues.Harvesting usually happens 10 to 24 months post-planting, depending upon the selection. The walking canes are reduced short, ensuring very little waste, and are promptly transported for refining to preserve sugar high quality
Geographic Circulation of Sugar Cane Production
The geographic distribution of sugar cane production is largely shaped by certain climate and soil demands. Significant generating countries, such as Brazil, India, and China, gain from tropical and subtropical environments that sustain the plant's growth. Understanding these variables supplies insight right into the international landscape of sugar cane growing.
Major Producing Countries
Sugar cane is grown in numerous areas worldwide, particular countries dominate production due to desirable environments and farming methods - sugar cane products. Brazil leads the worldwide market, representing about one-third of total production, thanks to its extensive haciendas and advanced farming strategies. India follows as a considerable manufacturer, taking advantage of both desirable climate condition and a large residential market. China and Thailand likewise place amongst the top producers, with reputable frameworks supporting their sugar sectors. Various other significant contributors consist of the United States, Mexico, and Australia, each leveraging their unique farming systems to boost outcome. These countries play a vital role in the sugar cane supply chain, affecting worldwide prices and schedule
Climate and Dirt Demands
Ideal environment and dirt problems are vital for successful sugar cane production. Sugar cane flourishes in exotic and subtropical areas, calling for warm temperatures between 20 ° C and 30 ° C (68 ° F to 86 ° F) These plants require abundant sunshine and rains, preferably between 1,500 to 2,500 millimeters each year, to guarantee peak growth. The dirt needs to be well-drained, abundant, and rich in natural issue, with a pH degree preferably in between 5.5 and have a peek at this site 8.5. Sandy loam or clay loam dirts are specifically for sugar cane farming, offering required nutrients and drainage. Geographical circulation is mainly affected by these aspects, with significant production areas located in Brazil, India, and China, where ecological problems line up with the plant's requirements for growth and yield.

Challenges Encountered by Sugar Cane Growers
Sugar cane farmers experience significant challenges that influence their resources. Climate change presents unforeseeable weather patterns, influencing plant return and quality. In addition, market rate volatility creates financial uncertainty, complicating long-term preparation for these agricultural producers.
Climate Change Impacts

How do environment change influences influence the stability of sugar cane farming? Increasing temperatures and erratic climate patterns significantly test sugar cane growers. Enhanced warm can lead to lowered yields, as the plants struggle to thrive in severe conditions. Furthermore, altered rains patterns cause either droughts or excessive flooding, both damaging to crop wellness. Pests and diseases are likely to proliferate in warmer environments, better threatening production. Dirt destruction and salinization due to increasing sea degrees can reduce cultivatable land. These weather adjustments urge farmers to adjust their practices, commonly needing financial investment in new modern technologies and durable plant varieties. Inevitably, the sustainability of sugar cane cultivation depends upon addressing these environment challenges successfully.

Market Rate Volatility
Market rate volatility offers significant obstacles for sugar cane cultivators, influencing their financial stability and preparation. Variations in market prices, driven by elements such as worldwide supply and demand, climate problems, and government plans, develop unpredictability for manufacturers. This changability makes it difficult for growers to forecast incomes and manage operating budget efficiently. In addition, when prices go down suddenly, many farmers might struggle to cover production expenses, resulting in possible monetary distress. To reduce these threats, some farmers transform to contracts or hedging techniques, yet these remedies may not be obtainable to all. As a result, market value volatility continues to be a relentless worry, influencing the total sustainability and success of sugar cane farming.
Comprehending the Sugar Cane Supply Chain
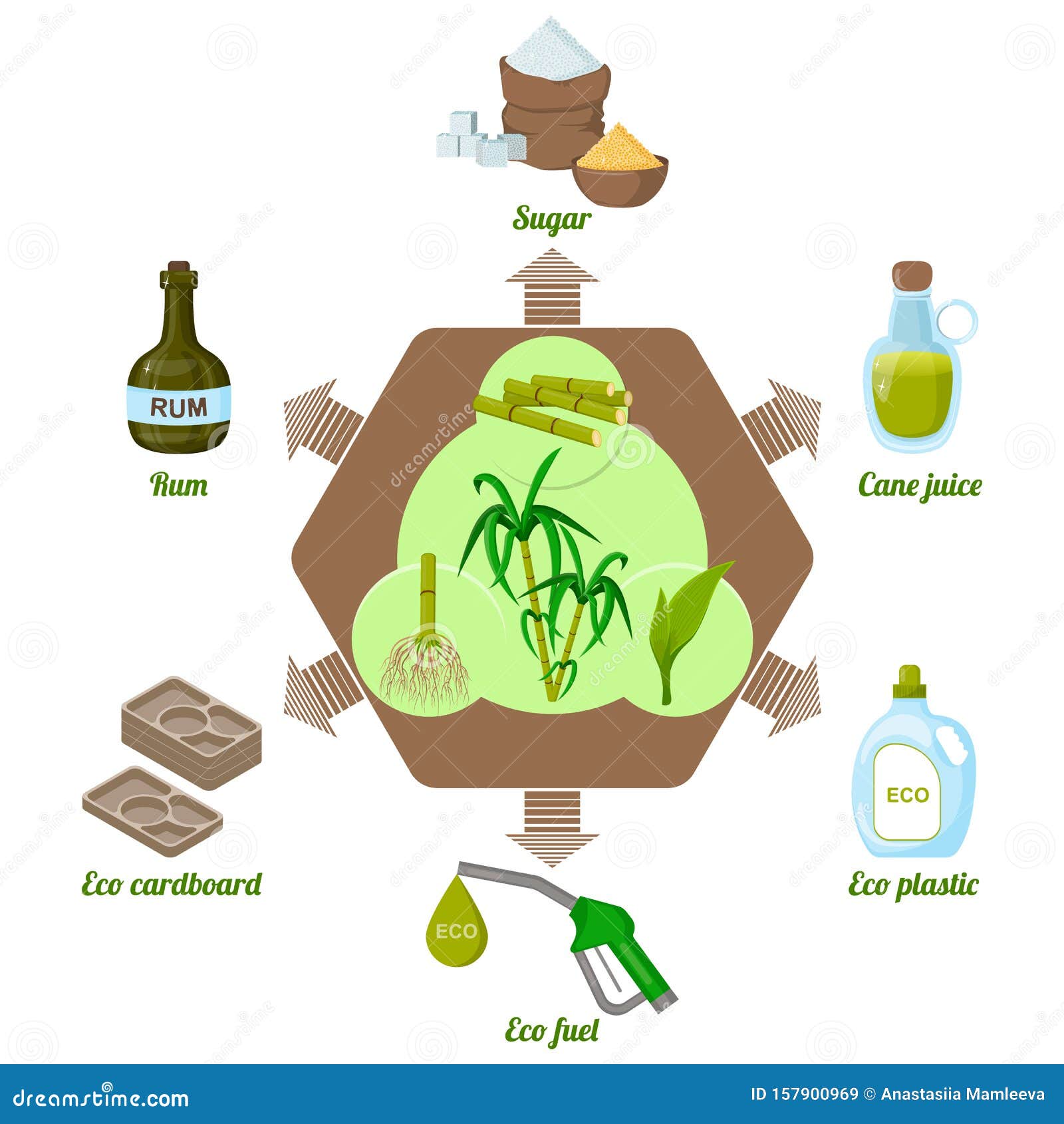
Market Fads Affecting Sugar Cane Rates
The dynamics of sugar cane costs are influenced by a range of market fads that mirror wider economic problems and customer behaviors. International need for sugar and sugar-related items plays an essential role, with raising interest in natural and sustainably sourced items driving rates higher. Additionally, fluctuations in oil costs influence the cost of production and transportation, further influencing market rates. Weather condition patterns are an additional substantial element; negative problems can bring about lowered returns and increased costs. Profession policies, tolls, and worldwide agreements likewise form the market landscape, affecting supply chains and schedule. Currency exchange prices can make complex global profession, impacting prices for both exporters and importers. Ultimately, shifts in customer preferences toward healthier choices may modify demand patterns, creating a surge result on sugar cane prices. Recognizing these interconnected patterns is crucial for stakeholders in the sugar sector.
Technologies in Sugar Cane Product Development
Numerous advancements in sugar cane product growth are improving the industry and expanding its applications. Researchers are discovering alternate usages past typical sugar, consisting of biofuels, eco-friendly plastics, and health and wellness supplements. Breakthroughs in enzymatic processing strategies have actually improved the removal of important substances such as antioxidants and vitamins from sugar cane, advertising its usage in practical foods.Additionally, the advancement of genetically changed sugar cane selections aims to improve return and resistance to parasites, while additionally improving the nutritional account of the plant. Innovations in fermentation processes have actually led to the production of top notch alcoholic useful site beverages obtained from sugar cane, attracting an expanding market for craft spirits.Moreover, sustainable methods in cultivation and processing are look here acquiring grip, with a focus on reducing environmental effects. These innovations not just develop brand-new market possibilities however additionally foster an even more lasting strategy to sugar cane production, straightening with worldwide trends towards environment-friendly items.
Regularly Asked Concerns
What Are the Environmental Impacts of Sugar Cane Farming?
The environmental influences of sugar cane farming include logging, loss of biodiversity, water pollution from fertilizers and chemicals, dirt destruction, and greenhouse gas discharges, all of which considerably add to ecological inequalities and climate adjustment.
Exactly How Does Sugar Cane Growing Affect Local Economies?
Sugar cane cultivation considerably affects regional economies by creating work, boosting farming industries, and producing earnings for farmers. Nevertheless, it can also cause financial reliance and fluctuations based upon market demands and environmental problems.
What Are the Key Pests and Diseases Affecting Sugar Cane?
The primary insects impacting sugar cane consist of the sugarcane borer and aphids. Illness such as red rot and smut considerably effect yield. Farmers have to carry out integrated bug administration techniques to reduce these dangers properly.
Exactly How Is Sugar Cane Processed Into Different Products?
Sugar cane processing entails crushing the stalks to extract juice, followed by explanation, evaporation, and condensation. This procedure yields raw sugar, molasses, and ethanol, each offering distinctive purposes in numerous sectors, from food to power.
What Are the Nutritional Aspects of Sugar Cane?
The nutritional aspects of sugar cane include necessary minerals and vitamins, particularly B vitamins, calcium, and iron. It also has fiber, though mainly made up of sucrose, which provides energy yet does not have substantial nutrients.
Report this page